For this month’s site feature, we’re headed to the top of the Northern Territory where one of Australia’s longest-running ecosystem flux monitoring stations is located. The Howard Springs OzFlux site has been operating continuously since 2001, diligently capturing carbon, water and energy exchanges from Australia’s productive, extensive and ecologically important tropical savanna ecosystems.
This year Howard Springs celebrates its 20th birthday—though the initial eddy covariance measurements were undertaken in October 1996—so this month’s story is a celebration of the extensive work that has been enabled by this historic flux tower.
The site was established by Prof. Derek Eamus (University of Technology Sydney) and is now jointly managed by Professor Lindsay Hutley at Charles Darwin University and OzFlux Director Professor Jason Beringer from The University of Western Australia. Alongside Lindsay and Jason, Matthew Northwood, also at Charles Darwin University, has been instrumental in keeping Howard Springs running for more than half of its life.
Pioneering research at Howard Springs
Howard Springs is located in a wet-dry mesic savanna ecosystem that is representative of most of the top-end of continental Australia. Rainfall is highly seasonal in the savannas, with approximately 90% of the mean annual rainfall of 1732 mm falling in the wet season months of October to April. This wet-dry dynamic has helped shape the savanna vegetation, which represents a co-existence between trees and grasses.
Investigations of the savanna ecosystem at Howard Springs began in the 1990s, where the fraction of ground water use by evergreen eucalypts was of critical importance for the sustainable use of the region’s groundwater resource. This was pioneering work led by Prof. Derek Eamus in collaboration with CSIRO and was one of the earliest studies using eddy covariance methods in a water resource management context.
Canopy scale work was complemented by a raft of studies examining the ecophysiological traits of the site’s different tree species, including photosynthesis and leaf conductance, leaf morphology and leaf area index, root biomass, transpiration, and ecosystem carbon and water fluxes from a temporary monitoring tower used to measure seasonal fluxes.
“I recall how hot the field work was – that hasn’t really changed!”
Prof. Lindsay Hutley, Charles Darwin University
The late 1990s and early 2000s saw the development of a collaboration with Professors Jason Beringer and Nigel Tapper, which continues to this day. Resources from Monash University awarded through an Australian Research Council (ARC) grant enabled the installation of a permanent flux tower in the dry season of 2001, allowing investigation of the impact of fire on radiation, energy and carbon fluxes in the savanna.
The permanent flux tower enabled more detailed continuous investigation of the inter-annual variability in carbon dioxide and water fluxes from the savanna, as well as how fire impacted these fluxes over time.
“We had a vision for keeping a long-term tower going but in the 10 years before TERN, we ran the tower from one small grant to the next, working many weekends and using student help to maintain a continuous record as best we could on the smell of an oily rag.”
Prof. Jason Beringer, University of Western Australia
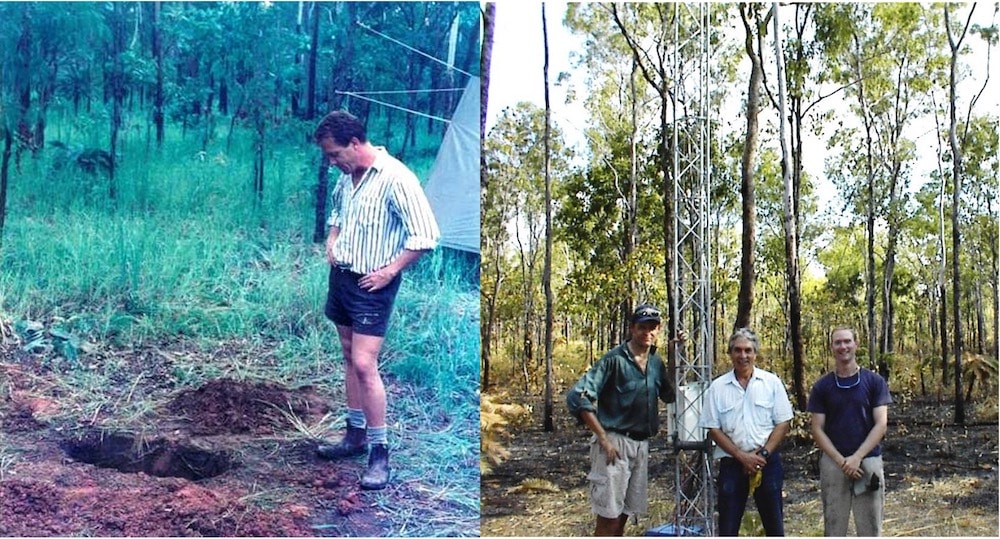

Left: Tony O’Grady contemplates the hand dug hole for the Howard Springs tower anchors during the early seasonal flux campaigns, March 1998 (credit: Lindsay Hutley), and right: Lindsay Hutley with Bert Tanner of Campbell Scientific and Lucas Cernusak of James Cook University at Howard Springs in July 2003 (credit: Lindsay Hutley).
Climate and fire shape savannas
Over time, the flux tower data and complementary ecosystem research efforts at Howard Springs have revealed the importance of climate and fire influencing physiological processes in Australia’s tropical savanna ecosystems.
The site has been particularly vital in documenting the seasonality of carbon taken up by the highly productive trees, grasses and shrubs that make up the ecosystem, but also where along the way this carbon is lost from the system during the dry season and from the frequent fire.
The main culprit for carbon loss is through fires, which are inevitable in savanna ecosystems—Howard Springs has a fire return rate of between one and three years.
Fires also impact on meteorological processes like the summer monsoon, which can affect savanna evapotranspiration. Less common disturbances are cyclones, which can damage large swathes of savanna as they cut across the landscape, and termites, which consume plant biomass and release methane in the process. By 2021, researchers using the site’s data are still refining carbon balance models, with recent work focussed on the carbon loss to the groundwater system, wetlands and the Howard River.
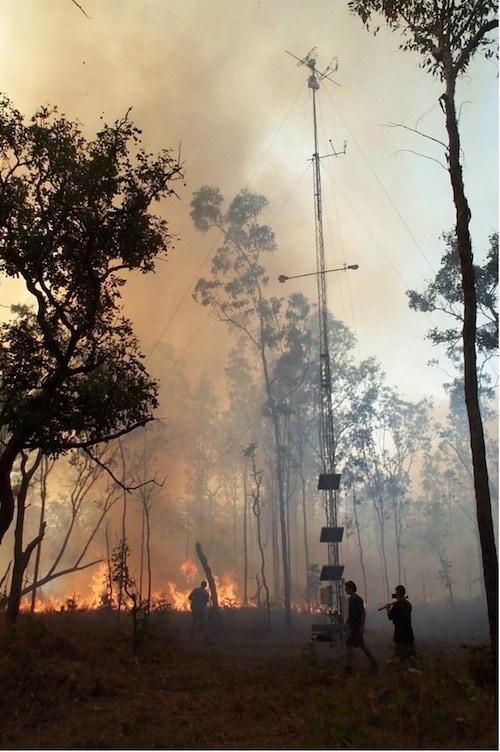

Controlled back burns are conducted at Howard Springs to reduce the risk of high intensity fires that could destroy the site’s sensitive monitoring equipment (credit: Jason Beringer)
“The long-term measurements collected at Howard Springs allow us to characterise the long-term Net Biome Production that takes into account the type, frequency and intensity of disturbance factors like fire, termites and cyclones.”
Prof. Jason Beringer, University of Western Australia
Howard Springs became a very well utilised and studied site by the mid-2000s, but there were still questions unanswered about how representative the site was of savanna ecosystems across Australia, and how savanna structure and function changed along the rainfall gradient from Howard Springs to Alice Springs.
In 2007, additional ARC funding enabled the extension of the work along a transect of monitoring sites called the North Australian Tropical Transect (NATT) in a large-scale field campaign called SPECIAL (Spatial Patterns of Energy and Carbon Integrated Across the Landscape).
Seven additional sites were established along the 1000 mm rainfall gradient moving inland from Howard Springs, led by Jason, Lindsay and Dr Peter Isaac. Howard Springs represents the northern-most site along this transect, providing a key piece in this new living laboratory to study spatial patterns of vegetation change over a prominent rainfall gradient.
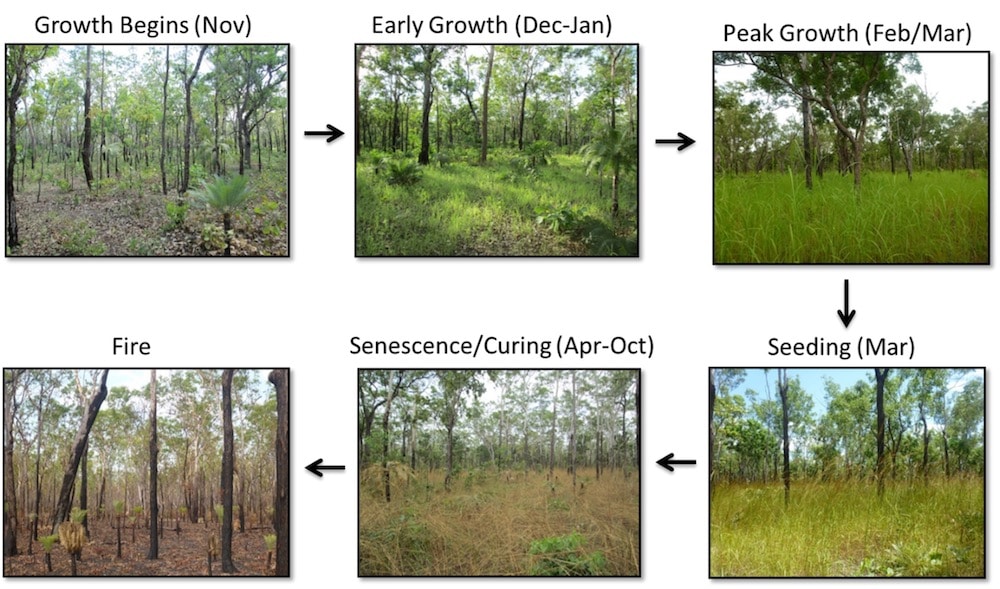
Seasonal changes in the understory at Howard Springs driven by plant life cycle traits, moisture availability and fire (credit: Caitlin Moore)
The future for Howard Springs
There is much to reflect on after more than 20 years of measurement from the Howard Springs site, and much still to learn about savanna ecosystems. Recent analysis at Howard Springs is showing a clear trend of CO2 fertilisation as the site’s 20th anniversary approaches in August 2021, and the longer the site continues, the more the usefulness of the data collected increases.
“As we approach 20 years, we are seeing strong long term increases in carbon uptake at the site that is correlated with increased precipitation, growing season length and higher CO2 levels. New research is needed to understand the drivers—such as CO2 fertilisation—for this change, and land surface models will be needed to attribute the changes that we see.”
Prof. Jason Beringer, University of Western Australia
Moving forward, it will be important to understand the role of climate change and disturbance (fire, cyclones, termites and invasive species and disease) on these systems and to grapple with complex interacting affects in the future.
In 2015, the TERN Litchfield Savanna SuperSite was established to complement Howard Springs in providing flux measurements from a similar Top End savanna ecosystem zone and so help in addressing some of these issues.







