SuperSites
Great Western Woodlands SuperSite
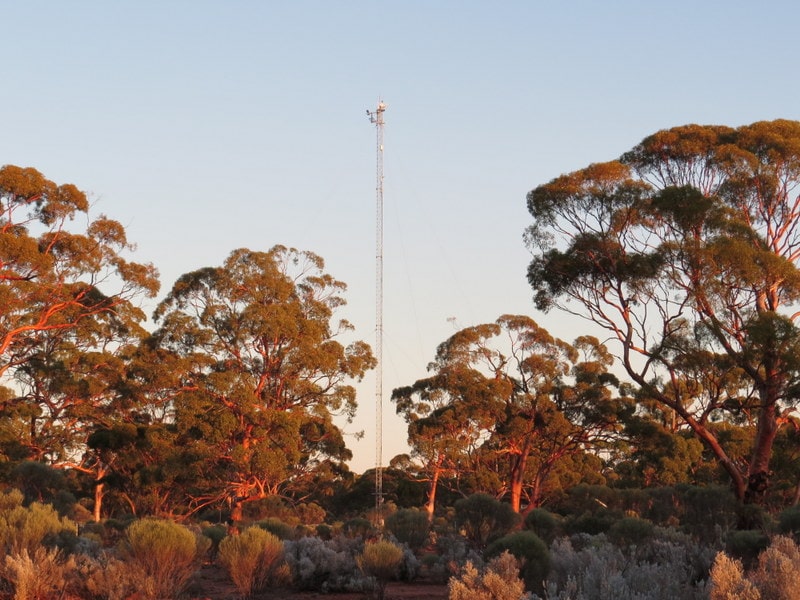
TERN’s Great Western Woodlands SuperSite is on Credo Station, a former pastoral property in Western Australia’s Goldfields region, near Kalgoorlie, Western Australia. The site lies in the internationally significant Great Western Woodlands region, which covers 16 million hectares in south-west Western Australia and is the largest remaining intact temperate or ‘Mediterranean’ woodland in the world. Native title claims of traditional ownership at this site have been registered by the Marlinyu Ghoorlie and Maduwongga Peoples.

Site Infrastructure & Characteristics
SuperSite Research Infrastructure
- One eddy-covariance flux tower
- Soil water content and temperature sensors
- Phenocams
- 13 x 1 ha Surveillance monitoring plots including along the South West Australian Transitional Transect (SWATT)
- Airborne LiDAR and hyperspectral imagery calibrated using SLATS star transects, leaf sampling, tree structure and LAI measurements
- 40 Nutrient Network plots

SuperSite Details
- Vegetation type: Temperate woodland, healthland and mallee vegetation, farming
- Elevation: ~450 m
- Rainfall: ~265 mm/yr
- Mean Temperature: ~18.8°C
- Soils: Red deep loamy calcareous duplexes
Site Research
Research using the Great Western Woodlands SuperSite relates to the impacts of climate change and management on the fundamental flows of energy, carbon, water and nutrient stocks, and on biodiversity, in semi-arid woodland ecosystems nationally and globally. Research questions include:
- Are old-growth semi-arid woodlands carbon sources or carbon sinks?
- From where do woodland eucalypts obtain their water?
- How do topographic mosaics regulate floristic composition and provide resilience to climate change?
- What are the ecological determinants of the Menzies line (the striking boundary between the Great Western Woodlands and mulga) and will it shift under climate change?
Featured Dataset
This dataset consists of measurements of the exchange of energy and mass between the surface and the atmospheric boundary-layer in temperate eucalypt woodland using eddy covariance techniques.
More Datasets
Site Partners


Research Publications
Since its inception, TERN’s infrastructure has enabled the publication of more than 1600 peer-reviewed scientific journal articles or books.






